The US government has officially ended the de minimis exemption (also known as Section 321) for all countries, meaning low-value imports under $800 will now be subject to duties and customs scrutiny. Read how it’s impacting ecommerce brands.
EU <> US trade deal is done. 15% tariffs on EU made goods and essentially 0% on US made goods. The China 30% tariffs received a 90-day extension (10% Baseline + 20% + section 301 stays in place for a least another 90 days).
If your brand is gaining interest from consumers in other countries it may be a sign that you should start shipping internationally. It can be a very lucrative point of growth, but one that requires rigorous planning to execute smoothly. International shipping is complex and it’s a big step for any ecommerce brand.
Whether you’re completely new to global shipping or you’re adding a new country to your international shipping mix, it’s important to first fully understand the tariffs, customs fees, and international shipping costs required. Accurate comprehension of these costs can substantially lessen any issues with budgeting and resource allocation.
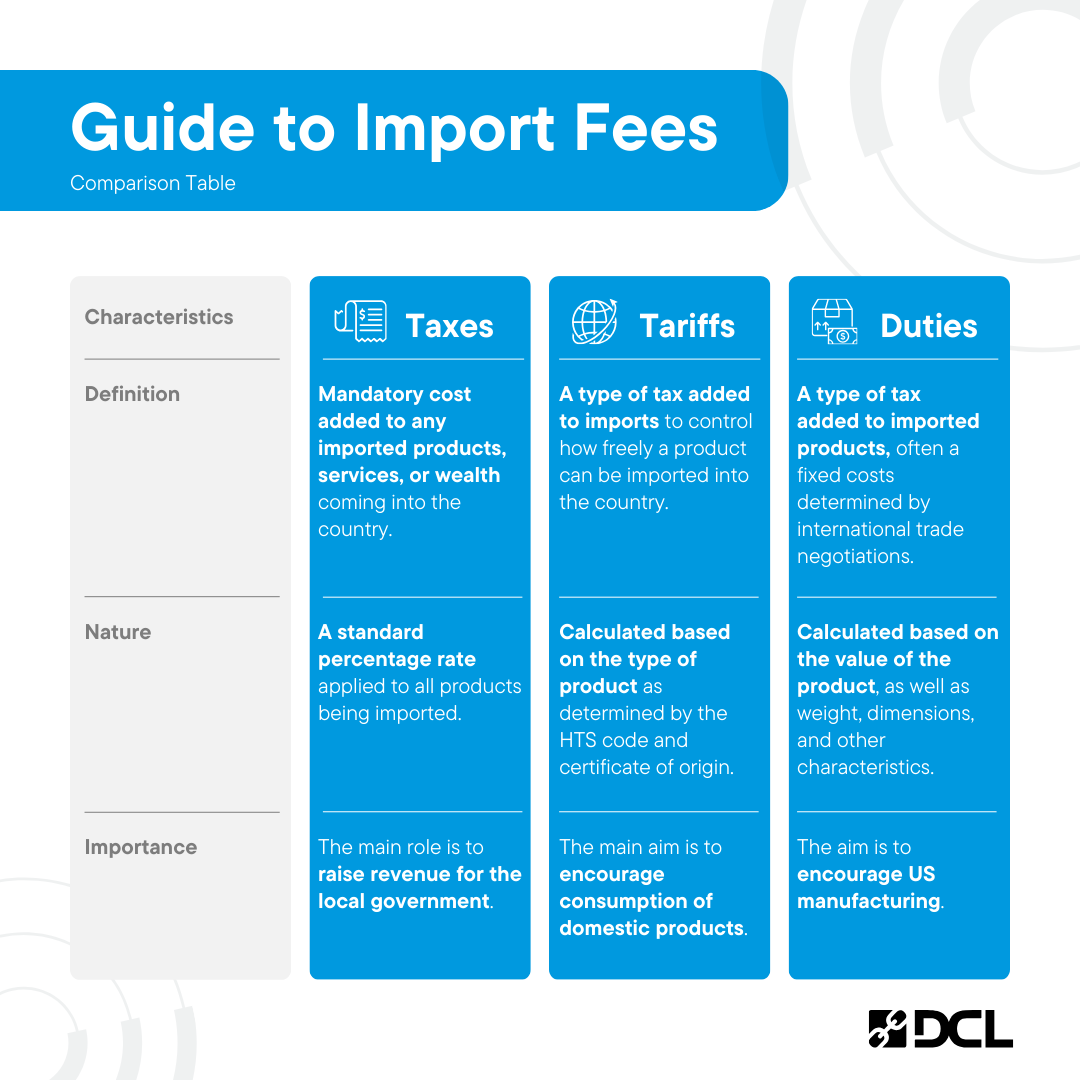
What's the Difference Between Tariffs and Taxes?
A tariff is a tax imposed on imported goods, typically intended to protect domestic industries and give a price advantage to locally produced goods over similar goods which are imported. Tariffs add to the cost of imported goods, making them less competitive with local products. These are often implemented as a fixed percentage of the value of the imported goods. They contribute to the revenue stream of the local government. Tariffs are also known as customs duties; the words tariff and duty can be used interchangeably.
For example, there is a current trade agreement between the US, Canada, and Mexico that there will be no tariffs on imports from any of the three countries—it’s called the USMCA trade agreement. Alternatively, with China there is a blanket 25% tariff (on top of any duties) given to any products imported into the US.
Here are the current US tariffs according to the Harmonized Tariffs Schedule (HTS).
Taxes are a separate (and often additional) fee defined and collected by the government or state where goods are being imported into. Import taxes are based on a standard percentage of the value of the imported product coming into the country.
There are various names for import taxes based on the country of import: Value-Added Tax (VAT) or Goods and Services Tax (GST). For example, The UK has a VAT rate of 20% and Australia has a GST rate of 10%. All VAT/GST are a flat percentage rate applied to all products being imported.

How are Tariffs Calculated?
All products will have different tariffs that depend on a combination of product classification, country of origin, and the country where the goods are being shipped. All tariffs are based on two main factors:
- The type of goods being imported, as classified by the correct HS Code.
- The international trade agreements between the country of origin and the country of import.
To determine the tariffs you’ll incur when shipping abroad, the first step is to accurately classify your products. The Harmonized System is a globally recognized standard of classification; every material has a corresponding code that can be identified. This code is an important part of customs documentation and labeling—HS codes help CBA (Customs and Border Patrol Agency) properly identify the customs process needed, tax and tariff rates, and any special shipping or handling that may be necessary.
Once you know the HS Code for your products, you can look up the corresponding tariff (duty) rate.
More resources for finding the tariffs specific to your products and country of import:
- IATA HS Code classification – https://uscensus.prod.3ceonline.com/
- Tariffs overview and resources – https://www.trade.gov/import-tariffs-fees-overview-and-resources
Reducing Tariffs: Strategies for Ecommerce Businesses
Tariffs can significantly increase the expenses associated with international shipping, causing a deterrent for new ecommerce businesses to start shipping abroad. Having a thorough understanding of current international trade agreements can help ecommerce businesses effectively manage and reduce the impact of tariffs on their bottom line.
Here are a few ways you may be able to reduce tariffs.
- Correct Classification. Accurately assigning an HS code to your products is a fundamental step towards reducing potential tariff costs. If you have an inaccurate classification, you may be overpaying, or underpaying which will result in fines and issues once you make any corrections.
- Modify Your Supply Chain. By procuring materials from countries with lower tariffs, or by manufacturing or assembling products in such countries, businesses can mitigate some of the cost burden of tariffs. Because tariffs can change quickly based on international trade negotiations, it’s important to consider future tariffs implications. Only take this strategy while also considering any potential disruption to your supply chain.
- Consider FTAs. A number of countries have established Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) that provide lower tariff rates, so it’s worthwhile for ecommerce businesses to consider markets where such agreements are in place. If it is not feasible to alter your sourcing and procurement, you can be more selective in the new countries you ship to.
- Hire an Expert. Partnering with an experienced international trade consultant can also provide valuable insights and assistance in navigating the complex world of international tariffs, ensuring compliance and minimizing potential risks. They’ll be able to analyze your international shipping and look for ways to help streamline and save on costs.
These strategies can be beneficial, but what is most important is tailoring them to your specific business needs and circumstances is key for optimal effect. The best thing you can do is understand the various trade agreements and regulations that are associated with them can make a substantial difference in your ecommerce brand’s bottom line.
Key Provisions of USMCA for Ecommerce Businesses
Understanding the mechanisms and implications of the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) is pivotal for small ecommerce businesses seeking to expand abroad. This significant international trade agreement replaced the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and brought about some pivotal changes that burgeoning ecommerce businesses must consider to manage international shipping costs.
The USMCA impacts many US brands because of large majority of both manufacturing and shipping brands do with both Canada and Mexico. This trade agreement was made in 2020 and created significant alterations to regulations that impact ecommerce businesses, including:
Increased De Minimis Thresholds: This provision has increased the minimum value of goods that can be imported tax and duty-free into Canada and Mexico. It directly benefits ecommerce businesses by reducing shipping costs for low-value shipments.
Digital Trade: The agreement prohibits customs duties and other discriminatory measures from being applied to digital products. This dramatically cuts costs for businesses selling digital goods and services.
Data Protection: The USMCA has robust protection regulations in place for transferring personal data across borders. This protects ecommerce businesses from unintended breaches of personal data.
It’s essential for ecommerce businesses to closely examine these modifications and to adjust their strategies accordingly to minimize costs and bolster competitiveness.
Like any international trade agreement, the USMCA carries with it an array of complexities and challenges—the increased de minimis thresholds is an obvious benefit, the requirements to closely monitor shipment values can be an administrative burden.
Resources and Tools for Ecommerce Businesses Navigate Tariffs
There are many resources for ecommerce businesses to help understand tariffs and international shipping costs.
The World Customs Organization’s (WCO). The WCO maintains the Harmonized System and provides comprehensive resources to understand product classification and associated tariffs. The WCO’s website offers a wealth of knowledge on harmonized system codes, duty rates, and much more, acting as a handy tool when you are establishing your international shipping strategy.
Country-specific Trade Organization. Each country has resources specific to their nees. Some examples include: U.S. International Trade Commission, the European Union’s Taxation and Customs Union, and Canada’s Office of the Auditor General. Here you can find databases that offer access to duty rates of different countries and regions.
Logistics and shipping experts. There are many independent experts you can reach out to for help. If you already work with a logistics or fulfillment provider, they may have insights into your brands that can help you make the best international shipping decisions possible. Major shipping carriers like FedEx, DHL, and others will also be able to help provide you with international shipping resources.
Trade Advisory Services are also valuable resources. They provide advice and guidance on import duty mitigation strategies, trade agreement utilization, and compliance with customs regulations. Working with a Trade Advisory Service, ecommerce businesses can leverage industry expertise to mitigate the impact of tariffs and effectively manage international shipping costs.

Tags: International









