Ecommerce businesses need to ensure fast delivery to customers at generally low costs. Freight carriers have taken note of this trend, and many carriers offer shipping services to meet these ecommerce expectations.
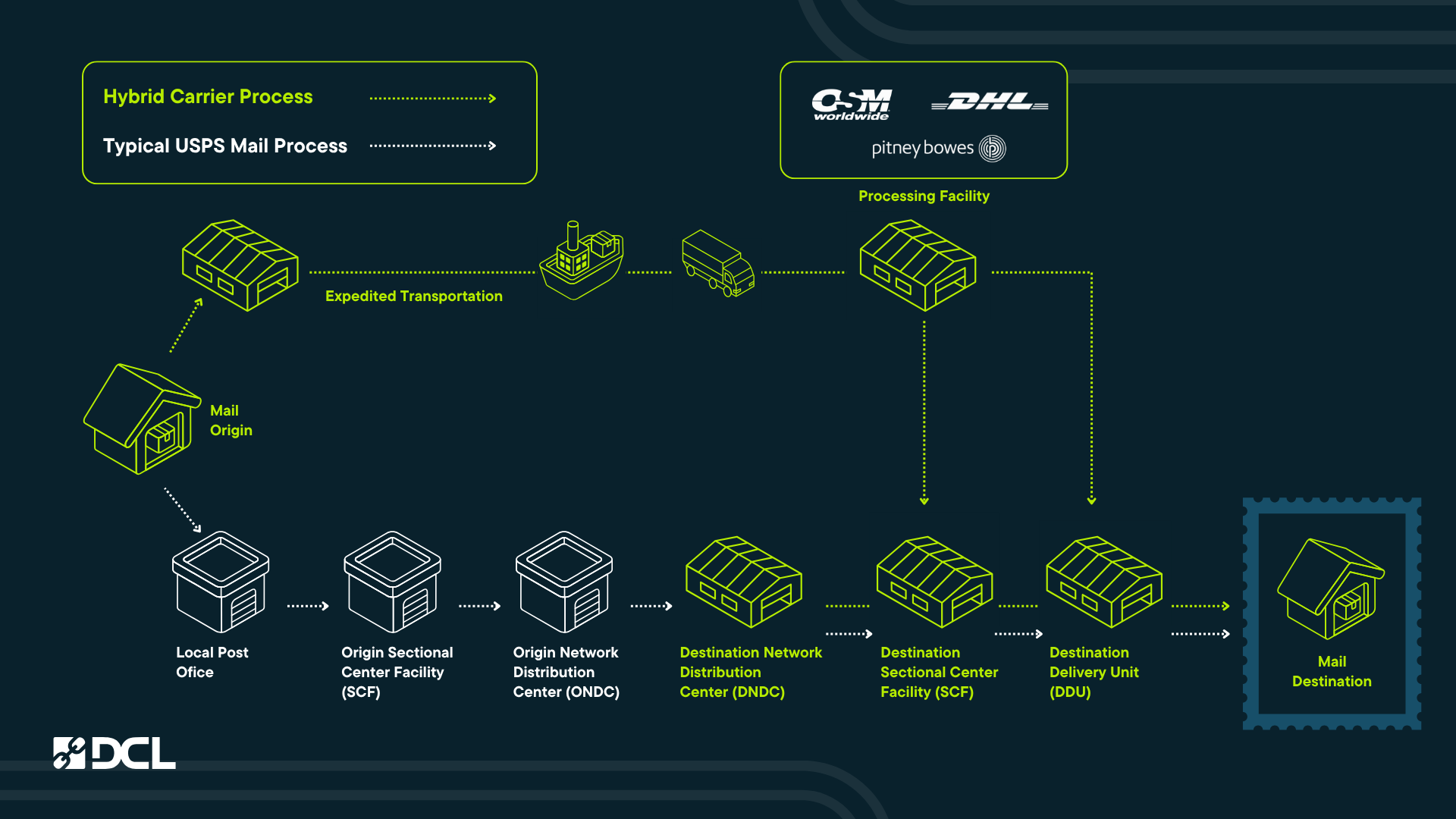
What is hybrid shipping service? The distinguishing feature of a hybrid shipping service is that it makes use of multiple carriers to transport a shipment. Most commonly a private carrier, like DHL or OSM, will receive a package, then transition it to USPS for the last leg of the shipping journey.
Most, if not all hybrid carriers and services use USPS for the last-mile. This is because USPS is historically the most reliable last-mile delivery carrier, with a very large network of infrastructure to deliver to the most addresses in the US of any other carrier. By leveraging this robust network and domestic infrastructure, private carriers are able to charge shippers a lower cost to get packages to more areas of the US.
Is hybrid shipping right for your ecommerce business? Large carriers like UPS and FedEx have shifted away from this model, while USPS has introduced a competitive service. While many brands choose this type of shipping, it’s not right for all products.
Examples of Hybrid Shipping Carriers and Services
There are many versions of hybrid shipping services. The most common examples are used by aggregator carriers that rely heavily on a hybrid shipping model, including:
- OSM Worldwide
- DHLeCommerce
- Pitney Bowes

How do Hybrid Shipping Services Work?
In basic terms hybrid shipping services use a combination of carriers to complete the transportation journey of a shipment.
Common examples of hybrid shipping services are DCL eCommerce, and OSM Worldwide. With each of these examples, the shipper works with the private carrier, DHL, who then outsources to another carriers (most often USPS).
For each of these examples, packages get handed off to USPS at either a sortation facility or post office, and USPS handles the final delivery.
Here is a full breakdown of steps shippers can expect when using a hybrid shipping service.
- Carrier with hybrid shipping service picks up shipment up from the brand or warehouse
- Packages get sorted at the carrier facility
- Packages may get moved to a regional facility closer to the delivery destination
- At any point packages will be passed to USPS at any of the following locations:
- Destination Delivery Unit (DDU)—the post office or wherever the USPS trucks pick up from to deliver your mail via established carrier routes
- Destination Hub (DHUB)—a facility in the USPS network that sorts and delivers to a group of DDU’s
- Destination Section Center Facility (DSCF)—a regional USPS distribution centers that feed the DHUB and DDU locations
- Destination Network Distribution Center (DNDC)—the farthest upstream in the USPS network, and feed the DSCF locations
Private carriers have long negotiated where within the USPS network they can inject parcels. The farther upstream in the USPS network, the less control the private carriers have over the parcel transit time, tracking and other considerations. USPS benefits from getting parcels sooner, but that can also create backlogs and delays.
What do Hybrid Shipping Services Cost?
Hybrid shipping services vary, much like any shipping services. There are many factors that affect the overall cost.
The carrier’s price depends on where packages are passed to USPS. The deeper they inject them in the USPS network, the less additional postage costs will be accumulated from USPS. That is because the carrier is actually doing some of the work for USPS.
Packages that are passed to the DNDC locations are the most expensive, and the price drops at each step closer to the DDU locations.
Some DDU locations support dense populations, such as New York City. Major carriers can inject large amounts of parcels at these Post Offices for the biggest bang for the buck. Very remote areas, however, might have Post Offices that are spread very far apart and serve very small populations. Carriers will not go to all of those if the parcel volume is too low. For those areas, injection would occur farther upstream (at DSCF of DNDC).
Benefits of Using a Hybrid Shipping Service
By using hybrid shipping services, ecommerce brands get the speed of a private carrier, but the reliability and wide network of USPS for last-mile delivery.
Here are some benefits shippers may get from using hybrid shipping services:
- Overall lower cost to transport packages
- Economy service
- Faster delivery service—generally 2-5 day transit time window
- Quicker delivery than using USPS only
- High quality of delivery reliability and tracking
It’s worth noting that shippers with high-volume lightweight parcels will get the most out of hybrid services. This means they can take advantage of USPS parcel select lightweight service, as well as over-a-pound shipments using USPS Parcel Select Service.
Reasons Hybrid Shipping is Not a Good Fit
With all shipping services, there are considerations to be made and tradeoffs for the benefits. Hybrid shipping services have limitations, here are some more obvious downsides.
- Transit times are not guaranteed.
- Heavy or bulky items are not a good fit.
- Additional handling or specialty shipping services may not work in tandem with hybrid services.
- Return shipping can be expensive.
It’s worth noting that refused or undeliverable shipments can be expensive. In addition to the postage, the USPS adds a service fee.
By contrast, using USPS Ground Advantage and USPS Priority Mail, returns come back for free. There are programs, however, that may significantly reduce hybrid returns costs. Directing the USPS to dispose of the return and receiving the data via an electronic file greatly reduces the cost. This is achieved through special ancillary endorsements on the shipping label.
Bottom Line
Why should ecommerce brands consider using a hybrid shipping service? Many companies may not understand exactly how they work. These shipping services are considered the work horse of ecommerce. Private carriers can move a high volume of medium and light weight shipments quickly and reliably, for a lower cost.

Tags: Freight









