Table of Contents
- Difference Between Vendor Central and Seller Central
- Defining Amazon’s Seller Central Programs
- Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)
- Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM)
- Seller Fulfilled Prime (SFP)
- Seller Central Fulfillment Chart
- How to Optimize FBA
- Overview of FBA Costs
- The Pros and Cons of Amazon FBA
- How to Optimize Amazon Fulfilled by Merchant?
- The Pros and Cons of Amazon FBM
- Tips for Combining FBA and FBM
- What is Multichannel Fulfillment (MCF)?
- General Tips for Selling on Amazon
- How to Win the Buy Box
- Optimize Amazon Product Listings
- Prepare for Amazon Prime Day
- How a 3PL Can Support Your Amazon Business
Whether you’re new to selling on Amazon, looking to switch Amazon seller programs, or seeking ways to grow your current Amazon sales—there are many factors to consider when choosing the right Amazon seller program for your brand.
Use this guide to determine which Amazon fulfillment model is right for your brand and your products.
Some brands choose to sell on Amazon when they should be looking for a 3PL to outsource fulfillment and logistics. While some Amazon seller programs will provide fast, reliable fulfillment support, brands may find the lack of individuality and loss of inventory control to be a detriment. You don’t have to choose between Amazon FBA or a 3PL—you can actually have both. Plus, the simplicity of fulfillment support through Amazon isn’t comparable to a 3PL, which can provide more comprehensive services and more dedicated support.

Difference Between Vendor Central and Seller Central
The most important difference between Amazon Vendor Central and Amazon Seller Central is the point of contact, who sells your products.
- Vendor Central—Amazon buys your products from you, then resells them to their customers.
- Seller Central—you sell your products directly to customers, through the Amazon marketplace.
Here is an overview of each service and when to choose which.
What is Vendor Central?
With Amazon Vendor Central you are considered a first-party seller, making this option often used by direct manufacturers and distributors.
Your brand becomes the supplier, selling your products directly to Amazon in bulk. Amazon then controls the pricing, fulfillment and sales of your products entirely.
Often times, sellers start with Seller Central and generate demand for their products to entice Amazon to buy their product in bulk through the Vendor Central program, like other ecommerce or brick and mortar retail channels (i.e. Walmart, Target, Best Buy).
Registration on Vendor Central is strictly by invitation only. If a company is selling through Vendor Central the phrase “ships from and sold by Amazon” appears on the order page.
What is Seller Central?
Seller central benefits are many. The Seller Central programs are open to all. They provide the seller more control of their own account, overall branding, connection with the customer, and pricing. They include quick payment terms and flexible logistical options.
Depending on the program you adopt, there can be drawbacks as well. There are limited advertising opportunities to boost sales and fulfillment costs can add up quickly.
If you choose to sell your products, there are multiple ways you can do so. You can choose from the following Seller Central programs, or create a strategy to combine them for various products: Amazon Fulfilled by Amazon (FBA), Amazon Fulfilled by Merchant (FBM), Amazon Seller Fulfillment Prime (SFP), Amazon Multi-Channel Fulfillment (MCF or Buy with Prime). More detail about these services is listed in the next section of this article.
Defining Amazon’s Seller Central Programs
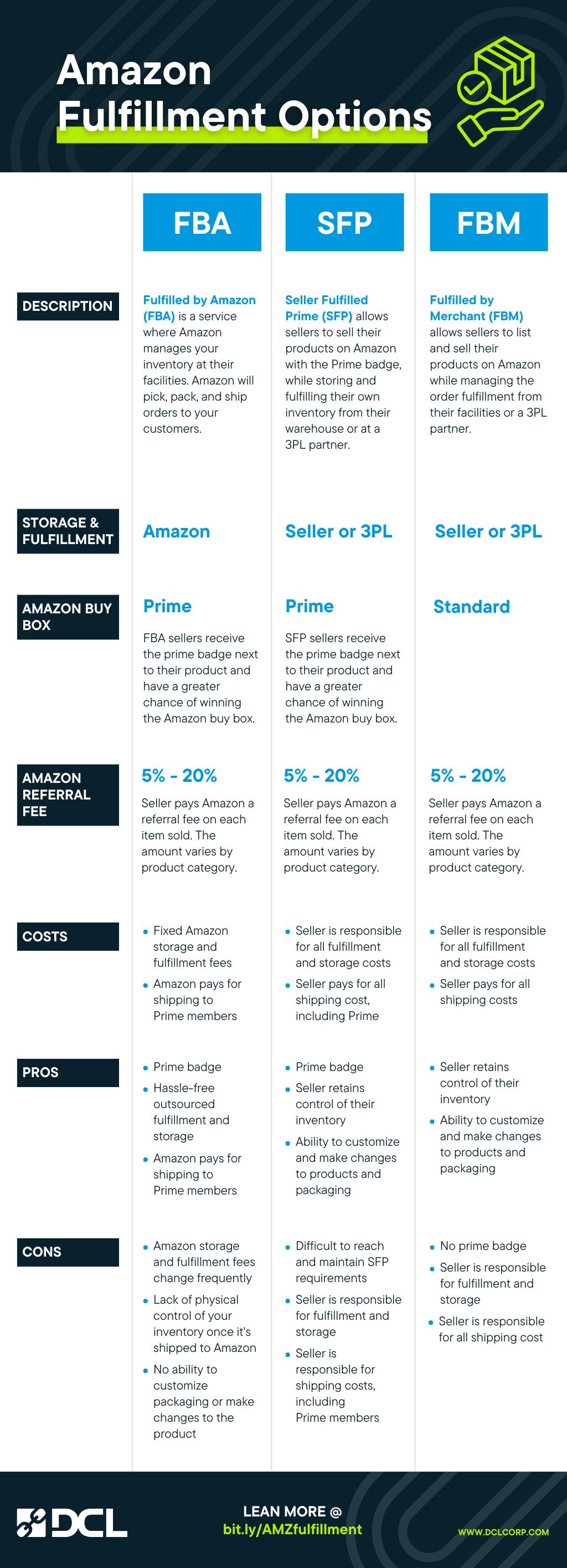
There are three core Seller Central programs for brands to choose from. Each has specific requirements and is best for certain types of businesses and products.
Here is a high-level overview of the Amazon’s Seller Central programs:
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)
With FBA, sellers send their products to Amazon’s fulfillment centers, and Amazon handles storage, packing, and shipping when customers place orders. It also provides customer service and handles returns. FBA sellers benefit from getting the Prime badge, giving them access to the 100 million prime subscribers and increasing their chances of “winning” the Amazon Buy Box.
- Best for: small, lightweight items, seasonal and fast-moving, products with international interest
- Worst for: products that heavy or oversized, highly regulated, or items with unpredictable demand
Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM)
Sellers using FBM fulfill orders themselves, managing storage, packing, and shipping independently. This allows for more control over the fulfillment process. The biggest difference is that FBM sellers do not get the Prime badge. The seller also needs to ensure they can keep up with Amazon’s performance requirements like shipping transit times and order accuracy.
- Best for: large or heavy products, custom or personalized items, perishable, fragile, or slow-moving products
- Worst for: fast-moving inventory, international demand, or items in highly competitive categories
Seller Fulfilled Prime (SFP)
SFP allows sellers the advantages of the Prime badge, while storing and fulfilling orders from their own facilities. Strict adherence to Amazon’s shipping and customer service standards is imperative and the seller is responsible for all costs related to storage, fulfillment, and shipping.
- Best for: high quality or branded packaging, private labeled and high-margin goods, perishables or fast-moving inventory
- Worst for: oversized, heavy, fragile, or slow-moving inventory, international or inconsistent demand
What is Fulfillment by Amazon
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) enables brands to sell products on the Amazon platform while outsourcing all labor, fulfillment, logistics, and shipping to Amazon. It means giving up a lot of control (inventory management and branding, primarily) to Amazon, but there can be cost benefits to outsource the unglamorous and time-consuming aspects of ecommerce.
FBA is a good program for many types of businesses, full-time ecommerce brands or those using Amazon as a side hustle.
If a brand chooses to use the Amazon FBA program, here are the actions that Amazon will take on for your business:
- Products are unpacked and stored in an Amazon warehouse
- When a customer purchases your product, their order is tracked through Amazon’s warehouse
- Amazon picks and packs your product
- Amazon ships your product to the buyer
- Amazon provides customer service for the buyer after shipment
Overview of FBA Costs
Cost is a big consideration and can be a deterrent for brand choosing FBA. When you outsource to Amazon, expect to pay a premium for their services. Here is an overview of the many costs and fees incurred by the Fulfillment by Amazon program.
Basic FBA Fees
FBA fulfillment fees cover picking and packing, shipping and handling, customer service, and product returns. Amazon FBA fees are charged per unit, but there are specific stipulations to calculate the price, it is based on the size classification of your product. Here are the size categories used:
- Standard size: products greater than 20 lbs. or smaller than 18x14x8 in. Fees vary, from $2.41 for products <1 lb. to $4.71 if it is >2 lbs. Anything over 2 lbs. is charged an additional $0.38 lb.
- Oversize: products that are larger than 18x14x18in. A “small oversize” might cost $8.13 if it is over 70 lbs. or over 60 in. on the longest measured size, plus the additional $.38/lb fee over the first 2 lbs.
- Special oversize: products categorized as weighing over 150 lbs. or having dimensions longer than 108 inches on the longest measured side, start at $137.32, with an additional fee of $0.91/lb. over the first 90 lbs.
For more details, see Amazon’s FBA pricing page.
If you want a clear assessment of FBA costs for a specific product, use this Fulfillment by Amazon Revenue Calculator.
Amazon Referral Fee
Amazon charges between 6%-20% of a product’s selling price, regardless of which fulfillment method is utilized. The fee is known as the Amazon referral fee. The actual percentage will depend on the category of the product you’re selling. For example, a computer accessory has a referral fee of 8% while a kitchen accessory is 15% of the total sales price excluding taxes.
Commonly Overlooked FBA Fees
There are many costs associated with the Fulfillment by Amazon program, and most are overlooked by brands new to selling on Amazon. Here are some commonly overlooked FBA fees.
- Apparel fees—all apparel incurs an additional $0.40 per item fee.
- Penalty fees—if any of Amazon’s strict requirements are not followed, you’ll get penalized.
- Unplanned prep fee—if a product is not properly packaged in direct accordance with Amazon’s guidelines (labeling, bagging, poly bagging, and taping) expect a fee for Amazon’s labor to correct it.
- Package prep fees—to avoid many penalty fees a brand can opt to have Amazon prep and package products for an additional fee.
- Return fees—if a product is eligible for “free” returns via Amazon Prime, a seller will have to pay an additional fee to facilitate those returns.
- Inventory removal fees—to have any of your inventory returned to you it costs between $0.50-$0.60 per item depending on size. If you wish to have Amazon dispose of items, it costs between $0.15-$0.30 per item.
Seasonal and Additional Fees
Expect added charges to be applied based on other factors. The most common fee is peak season, which is charged during Q4, a time of high order volume. In fact, peak season can bring a host of challenges to FBA members, storage restrictions and fees are only part of it.
You may also see extra fees for the length of time your products are stored (long term inventory), and other ad-hoc qualifications.
The Pros and Cons of Amazon FBA
Brands considering the Fulfillment by Amazon program should look at their product type and their customer needs. Prime benefits, customer service, and returns management are the biggest reasons to choose FBA. But if these aren’t necessary for your sales success, FBA may not be the right Amazon program for your brand.
Advantages of FBA
- Prime Eligibility. Access to Prime 2-day shipping which can significantly reduce cart abandonment.
- Customer Trust. Amazon’s reliable shipping, customer service, and simple returns can enhance customer trust.
- Time Savings. Amazon handles picking, packing, and shipping orders, saving you time.
Disadvantages of FBA
- Fees. Expect storage fees, fulfillment fees, and many more, which can impact overall profitability.
- Less Control. You’ll be at the mercy of Amazon’s fulfillment process, and there’s a risk of commingling inventory with other sellers.
- Strict Rules. Failure to adhere to Amazon’s rules (i.e. receiving requirements) may result in noncompliance charges or refusal to deliver your product.
- Sales Tax Compliance. Your products may be housed in Amazon fulfillment centers in different states, based on your customer base at any given time, making sales taxes complex.
There are also many storage considerations with FBA—the program has been known to implement storage restrictions to FBA customers at their own discretion.
If Amazon FBA doesn’t seem like a great fit for your brand, there are many FBA alternatives to consider.
What is Amazon Fulfilled by Merchant (FBM)?
Fulfilled by Merchant (FBM) is an Amazon program that allows ecommerce businesses to sell products on the Amazon platform but store, fulfill, and ship orders in-house or via a third-party fulfillment provider.
When Amazon sellers use FBM, they’re required to handle the fulfillment of items they’ve sold from their inventory. This means managing or hiring a network of warehouses to support your sales as well as overseeing the entire fulfillment process, from picking to packing and physically moving items to their final destinations.
Instead of paying Amazon to manage your inventory and pick/pack process, the brand is responsible for all aspects of the fulfillment and logistics of your Amazon sales.
It is common for brands to use a 3PL to manage their FBM program.
The Pros and Cons of Amazon FBM
Fulfilled by Merchant is a better program for brands who want more involvement in the overall process of selling.
Advantages of FBM
- Cost Control: More control over fulfillment costs. Potential to save on storage and fulfillment fees.
- Inventory Control: Manage your own inventory and monitor stock levels more closely.
Disadvantages of FBM
- Shipping Speed: You may not be able to offer the same speed as FBA, potentially affecting customer satisfaction.
- Prime Eligibility: Non-FBA products may not be eligible for Prime, impacting visibility and sales.
Tips for Combining FBA and FBM
By combining Amazon fulfillment programs, you can get the best of FBA and FBM without the drawbacks. You gain access to all the benefits of Amazon’s fulfillment for your FBA ASINs along with the perks of managing the process from beginning to end for your FBM listings.
With a combination of FBA and FBM you may see the following benefits:
- Increase efficiency—maximize your FBA perks by strategically choosing items for FBA, then use FBM for the products that are more cost-efficient through self-fulfillment.
- Reach more customers—FBA offers access to Prime customers, so even if you can’t feasibly use FBA for all of your products, customers who like what they get through your FBA listings may find you in other places for your other products.
- Reduction in administrative workload—by using FBA you’ll free up time and resources that previously went into fulfillment, put those toward iterating products or growing your business.
Tips for Setting Up Both FBA & FBM
Establish your FBA program—choose the priority products that fit well within the FBA model (fast selling inventory that ships easily).
Create mirror FBM listings—with some products in FBM they’ll always be there even if your FBA listings sell out.
Optimize your FBA inventory strategically—FBA has strict inventory limitations, so reserve slow moving products for FBM so they don’t take up precious space in your FBA stock limits.
Iterate, optimize, and grow—by combining both programs you’ll be able to keep your business defensible and get access to the worldwide logistics and marketing machine that is Amazon.
By leveraging the two fulfillment methods strategically, you can choose the most cost-effective and convenient options for your business as well as your customers.
What is Multichannel Fulfillment (MCF)?
Multi-Channel Fulfillment gives ecommerce brands the option to sell products through Amazon via their own site or a third-party platform. Through MCF, brands also benefit from Amazon’s fulfillment, logistics and shipping services. It’s a full-service fulfillment program, but it gives sellers the opportunity to bring customers in through their own branded site.
Here’s the flow of how MCF works:
- Consumers will see a “Buy with Prime” attribute when they go to purchase products on the brand website, or other ecommerce platform.
- The consumer is taken through the Amazon cart flow to finalize the purchase.
- Amazon receives the order and proceeds to fulfill and ship it from their warehouse.
- The brand is responsible for any customer communication follow-up, returns, or customer service issues.
The main advantage of MCF is that it gives businesses more control over their branding, but leverage Amazon’s extensive fulfillment network. Consumers get the speed and reliability of the Amazon promises, and brands have a hands-off way of outsourcing fulfillment and shipping.
Brands who experience high levels of demand through their own branded ecommerce platform will find MCF the most beneficial.
There are some downsides to MCF. Namely that consumers may find it too cumbersome to click through a multi-step checkout process. There are also considerations to make for follow-up communication and returns, which are the brand’s responsibility through MCF.

General Tips for Selling on Amazon
One thing all Amazon sellers know is that it’s a dynamic platform to sell on—which means you’ll have to make sure you’re always optimizing your product presence. Before you can do that, it is critical to ensure it’s the right platform for your brand. There are many ecommerce online marketplaces that may suit your products, customers demographics, and brand needs much better.
Amazon is not best suited for products that are highly competitive, especially price competitive.
If your products do well on Amazon, then you’ll surely see growth. The better they perform (based on sales volume, customer satisfaction, reviews, and more) the more Amazon will promote them in search.
Here are some expert tips to keep your Amazon sales strong.
How to Win the Buy Box
The Buy Box is a prioritized product placement on Amazon (as well as some other online marketplaces). When consumers search for a generic product, the Buy Box will be served to them first even if there are many listings that exist for the same or similar products. It’s a big promotional tool for brands who choose to go after it—whether through paid promotion or sales strategy.
Here are some determining factors for winning the Buy Box on Amazon:
- Low price usually wins the buy box, but it’s not the only factor.
- How fast you can ship your products is huge. Fast shipping will be rewarded by the platform itself, plus you’re more likely to receive positive customer reviews (which also increases the buy box potential!).
- How fast you can respond to customer queries and issues looks very good in the eyes of the platform, and your customers.
Brands can also pay to get the buy box for a select period. This is often used as a strategy around an important sales cycle or product launch, if you know your products won’t meet the above criteria naturally.
Best Ways to Optimize Amazon Product Listings
Amazon may be a black box to some, but the rules and requirements to sell successfully on the platform are simple. Grow your Amazon sales by optimizing your listings.
- Maintain fast shipping. The entire reason Amazon came to be what it is today is fast shipping. If you are using any of the Amazon programs that require in-house shipping, be sure you can match or beat Amazon’s 2-day delivery.
- Positive customer reviews. The more 5-star reviews you can net, the better you’ll perform on Amazon. Keep your customers extra happy by making all listings very clear (dimensions, uses, etc.), fulfilling for safe and quick delivery.
- Automate your content. Wherever you can, automate your listings—for language translation, currency conversion, product changes, etc. The less manual work that goes into updating your product listings, the better.
How to Prepare for Amazon Prime Day
Amazon Prime Day has become a global shopping event, like its own Black Friday for Prime Members, and is likely one of the biggest sales days of the year for most Amazon sellers. This annual extravaganza usually lasts two days, and the exact dates are still yet to be released.
Two of the biggest factors that will determine the success or failure of Prime Day sales are inventory and pricing. Here’s how to factor both into your Prime Day Sales strategy.
If you anticipate higher volume sales, stock-up on inventory. Treat Prime Day like any major holiday sale. Incorporating lead time into your forecast is crucial.
Before you get too caught up in Prime Day sales and try to offer the lowest price on the market, take a step back and factor in your total costs. Discounts and promotions are heavily encouraged, but it’s important to remember Prime Day isn’t a race to offer your products at the lowest prices. Many sellers have made the mistake of offering prices far below what would be profitable for them, which will lead to a decline in overall revenue.
How a 3PL Can Support Your Amazon Business
If you already outsource fulfillment or inventory management to a 3PL, they should be able to help support your Amazon business as well. Even though Vendor Central and Seller Central programs are completely different, there are many benefits brands can get from using a 3PL to support their Amazon sales.
A 3PL ships to many retailers, so if you are looking to include Amazon in your omnichannel ecommerce strategy, using a 3PL to support your Amazon sales will help consolidate your fulfillment under one roof. You’ll also benefit from more flexibility with your inventory.
An experienced 3PL will be able to meet Amazon’s strict requirements to help you efficiently manage your inventory so you can get your products to your customers faster and more cost efficiently.
Here’s a summary of how a 3PL can support each service:
- Vendor Central—A 3PL will be able to help centralize and distribute your inventory to various retailers, including Amazon. Choose a partner who has experience fulfilling under Amazon’s strict requirements.
- Fulfillment by Amazon—A 3PL who can meet Amazon’s strict requirements 100% of the time will help relieve you of penalty fees, and likely offer lower storage fees, especially when dealing in bulk.
- Seller Fulfilled Prime—A 3PL will help manage Amazon’s strict requirements, including setting up the Amazon integration and meeting performance demands like delivery times and order accuracy.
- Fulfilled by Merchant—Very similar to SFP, but without the benefits of the Prime badge, a 3PL can help smooth out the operational requirements and limit any customer issues or noncompliance penalties.
This post was written by Maureen Walsh, Marketing Manager at DCL Logistics. A writer and blogging specialist for over 15 years, she helps create quality resources for ecommerce brands looking to optimize their business.
Tags: Expert Advice & Tips, Fulfillment Costs, Omnichannel Fulfillment, Online Marketplace












